Associate this model of blocks with the geometry¶
Associate the model to the geometry means that the geometry to mesh is “raw” for this application. In other words, there will be no modification of this geometry end no rebuild of a complete new geometry. However it is possible to complete this geometry by adding new pieces if necessary without any topological operation to link these pieces to the initial geometry. Generally, the geometry to mesh is defined as a set of faces, if these faces are not given under solid form but form logically this solid, it is sufficient for this application.
To associate the model to the geometry, three successive steps are to be followed:
- Mandatory: associate all the vertices of the model to the geometry
- If necessary: associate the needed edges of the model to the geometry
- If necessary: associate the needed faces of the model to the geometry
The HexaBlock application enables to follow these three steps independently (see Elements association). To facilitate the association of the model to the geometry, an alternative way exists: the first two steps above can be replaced by a new stage called association by lines (see Association by lines).
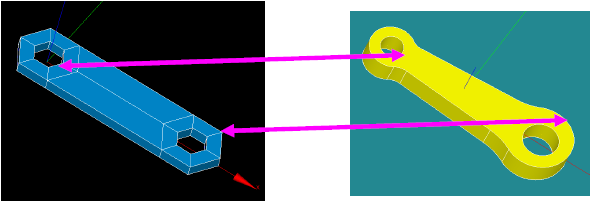
Rod connecting
Elements association¶
Associate the vertices¶
This step is essential, all the vertices of the model must be associated to the geometry.
There are 4 ways for this association:
- associate one vertex “v” of the model to a “vertex” of the shape “s” of the geometry.
- associate one vertex “v” of the model to a point of curvilinear abscissa “p” of the “edge” included in the shape “s” of the geometry.
- associate one vertex “v” of the model to a point of coordinates “u,v” of the “face” included in the shape “s” of the geometry.
- associate one vertex “v” of the model to a any point.
It is possible to examine the association (vertex of the association model, x-y-z-coordinates of the point of the association geometry).
For each vertex, the association is made in three steps:
Choose a vertex of the model to associate.
Choose the way of associating among the 4 possibilities described above.
- Specify the point on the geometry, the process depends on the previous choice:
- case of an existing vertex: selection and highlight on the vertices of the geometry solely
- case of a point taken on an edge of the geometry: selection and highlight of the edges and of a point on the edge in the process of being selected.
- case of a point taken on an face of the geometry: selection and highlight of the faces and of a point on the face in the process of being selected.
- case of a new point: ask the coordinates and visualize this new point.
Associate the edges¶
This step is optional. An association of every edge is determined automatically before generating the mesh. This automatic process applies four different algorithms in the following order:
the first algorithm determines a wire between the two vertices by taking the shortest way.
- if that wire does not exist, then another wire is build in the following manner:
- compute the normals to the two vertices,
- compute the mean normal of the two previous normals,
- build the plan passing through the two vertices and this mean normal,
- the sought-after wire is the intersection of the geometry with the plan,
if the intersection with this plan fails, then another wire “iso-type” is determined between the two vertices and going along the faces of the geometry linking these two vertices,
if this wire still does not exist, then the vertices are linked by a line segment.
If one of the automatic choices is not appropriate, then the association of the edge of the model to the geometry has to be defined explicitly.
Associate the quadrangles¶
This step is optional. The model quadrangles association is automatic. The three cases are processed:
all the geometric faces exist then the nodes are computed on these faces,
- the faces do exist but some pieces are missing because of the new edges or vertices, in that case two strategies are deployed:
- automatic construction of the missing faces from the contour lines,
- or association of new faces build in the geometry,
- there are no associated faces to the quadrangle of the model:
- only the automatic mesh is used,
- if this automatic mesh does not work, then it is possible to associate to the model quadrangle a geometric face build in GEOM by the user.
If one of the automatic choices is not appropriate, then the association of the quadrangle of the model to the geometry has to be defined explicitly.
Association by lines¶
The description of this step is:
- At the end of this new stage, it is necessary that all points of the model blocks are associated with the vertices of the geometry,
- The process is to associate the lines of the model of blocks to vertices and edges of geometry until all points of the model of blocks are associated,
- When all points of the model of blocks are associated, it is still possible to complete with step 2 above (see Associate the edges) to finish the association of needed edges.
See TUI scripts and GUI part.