Version: 8.3.0
The main purpose of this module is to propose a set of algorithms for mesh interpolation fully independent of the mesh data structure to support several type of format. This component is parametrized as much as possible using C++ templates. For the moment only interpolators for unstructured meshes are present in the interpolation kernel.
In the interpolation kernel, algorithms that computes the intersection 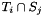 given the locations and geometries of source cell
given the locations and geometries of source cell 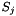 and target cell
and target cell 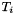 are called Intersectors and point locators.
are called Intersectors and point locators.
As can be seen in the theory of interpolation, all the proposed interpolators aim at filling the interpolation matrix W (which is generally sparse). For each pair (i,j), 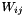 is obtained by calling the desired intersector. The problem is that each call to this algorithm is CPU-expensive. To reduce the computational time, a first filtering is done to detect pairs (i,j)
is obtained by calling the desired intersector. The problem is that each call to this algorithm is CPU-expensive. To reduce the computational time, a first filtering is done to detect pairs (i,j) 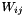 is obviously equal to 0. It is typically the case when a cell in the source mesh is too far from an another cell in the target mesh each.
is obviously equal to 0. It is typically the case when a cell in the source mesh is too far from an another cell in the target mesh each.
So for a given type of interpolation, the computation of W is performed in two steps :
Whatever its dimension and type, each interpolator inherits from INTERP_KERNEL::Interpolation which is a template (CRTP) class than enable an easy access to the main API without useless CPU cost.
Each Interpolators and Intersectors are parametrized (templated in C++ language) with class MeshType . This type of generalization has been chosen to reduce at maximum overhead.
Thanks to this principle intersectors and interpolators are usable with several mesh formats such as MED or VTK, without performance loss. MeshType is a concept that should strictly fulfilled the following rules :
int or long int .![$ [0,n-1] $](form_77.png) ) or FORTRAN (
) or FORTRAN ( ![$ [1,n] $](form_78.png) ).
).getCoordinatesPtr must be a full interlace array.getConnectivityPtr and getConnectivityIndexPtr must be with the same principle as it is implemented in MEDCouplingUMesh. Of course the numbering format may change according to My_numPol policy.Note that the array format for connectivity is kept close to MED. It is close to VTK format too but slightly different. So it may require for the VTK side a copy on wrap. To avoid this copy of a part of the connectivity structure, an iterator should be used.
As already said, the matrix returned by interpolator is typically a sparse matrix. Instances of class MatrixType are used to store the resulting interpolation matrix. To be able to be filled by the interpolator the MatrixType class has to match the following concept :
class Row has to match at least the following concept :
Note that std::vector is a candidate for < std::map<int,double> >MatrixType.