Version: 8.3.0
The MESH module contains a set of meshing algorithms, which are used for meshing entities (1D, 2D, 3D sub-shapes) composing geometrical objects.
An algorithm represents either an implementation of a certain meshing technique or an interface to the whole meshing program generating elements of several dimensions.
For meshing of 1D entities (edges):
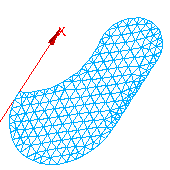
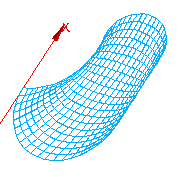
For meshing of 2D entities (faces):
For meshing of 3D entities (solid objects):
Hexahedron (i,j,k) meshing algorithm - solids are split into hexahedral elements thus forming a structured 3D mesh. The algorithm requires that 2D mesh generated on a solid could be considered as a mesh of a box, i.e. there should be eight nodes shared by three quadrangles and the rest nodes should be shared by four quadrangles.
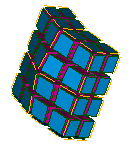
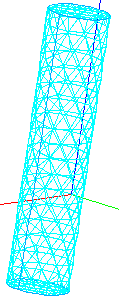
Some 3D meshing algorithms, such as Hexahedron(i,j,k) also can generate 3D meshes from 2D meshes, working without geometrical objects.
There is also a number of more specific algorithms:
Constructing meshes page describes in detail how to apply meshing algorithms.
See Also a sample TUI Script of a Define Meshing Algorithm operation.